

sql file in any editor (Notepad), Which you imported from the MYSQL server. To convert both the character set and collation of a string, use CONVERT() to change the character set, and apply the COLLATE operator to the result: mysql> SET. and: IF a string column is added that does not specify either CHARSET or COLLATE clauses: the behavior and performance will be different. SELECT FROM tablename WHERE username 'Warrior' It only returns me the rows where username 'Warrior', 'warrior' or 'WARRIOR', and not 'WRROR' 'Wrror' etc. Although database systems usually do permit altering the collation of an existing database, doing so can lead to complications it is recommended. I am looking for a charset/collation that would make it so when I do a. To solve this error follow the step guideline: In their current form: the behavior and performance of t1 and t2 should be identical. For example, the default server-level collation in SQL Server for the 'English (United States)' machine locale is SQLLatin1GeneralCP1CIAS, which is a case-insensitive, accent-sensitive collation. Collatie in de praktijk (2): Dezelfde lijst, maar nu in Bash.

Collatie in de praktijk (1): Deze lijst komt uit Nemo. MySQL implements several types of collations: Simple collations for 8-bit character sets.
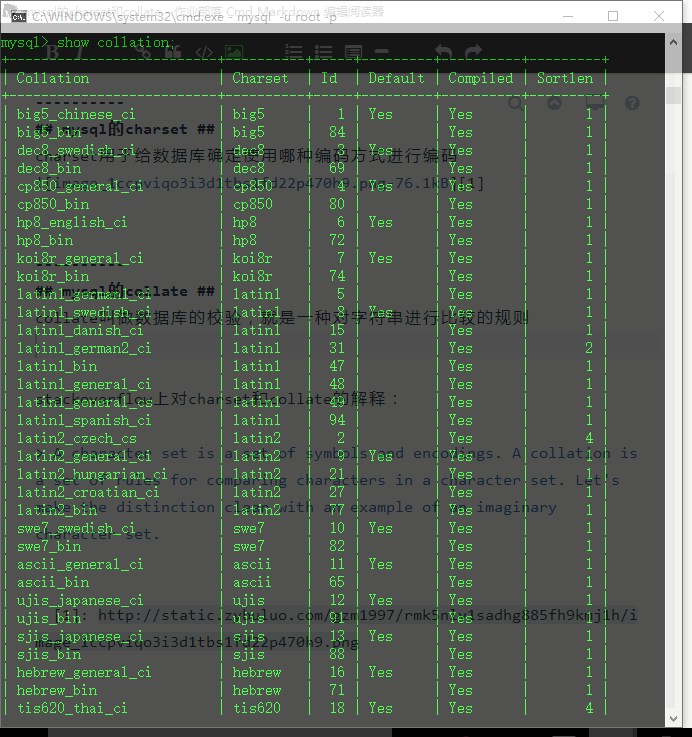
MySQL behandelt karaktersets en collation vaak tezamen. Some rules that need to put in mind are that: Two. Dit is overigens de enige reden waarom ik me ben gaan verdiepen in deze materie.
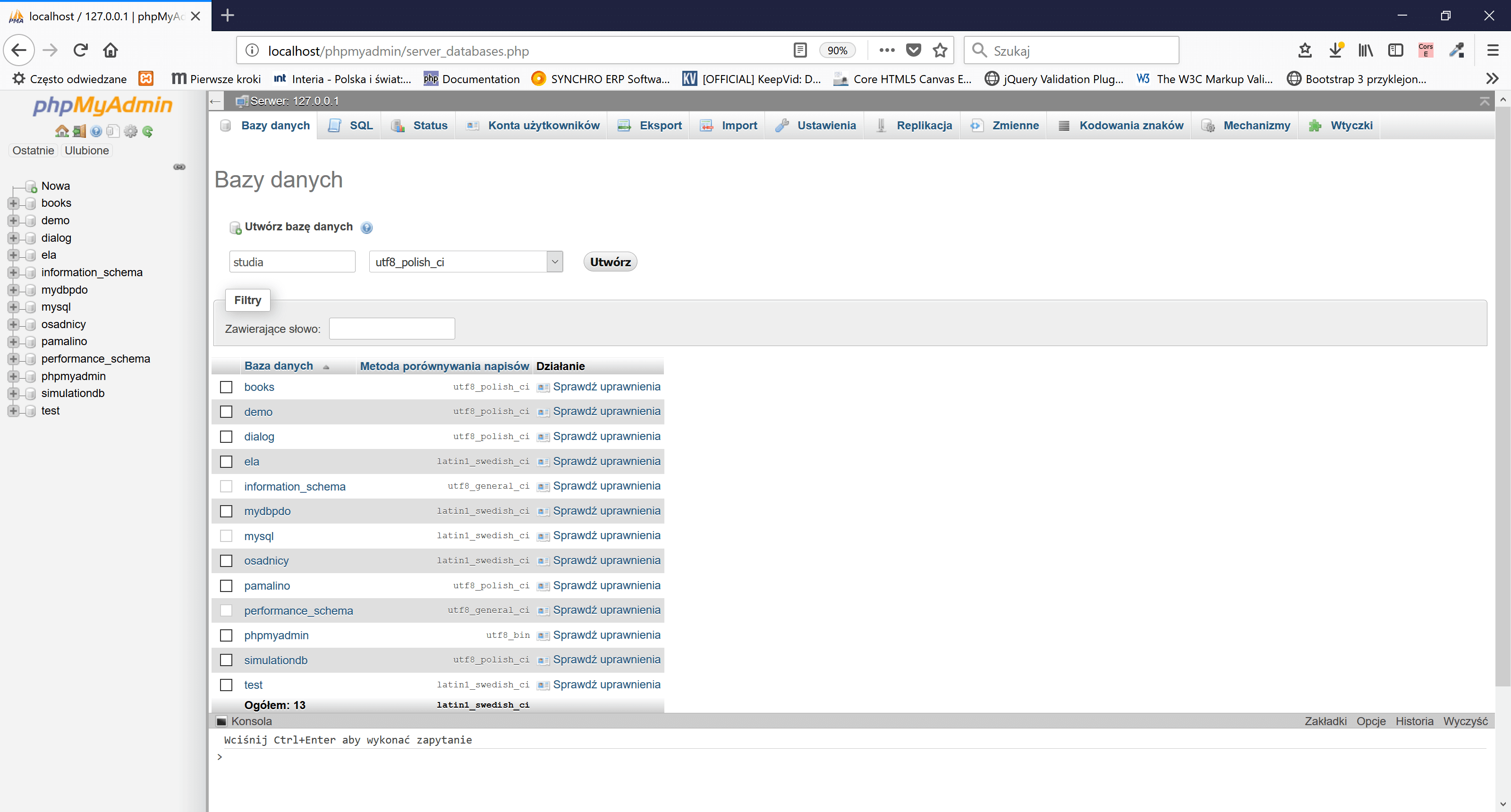
The character set and collations can be set at four levels and they are at: server level, database level, table level, and column level. Historically, MySQL and derivatives used utf8 as an alias for utf8mb3 - MySQLs own 3-byte implementation of the standard UTF8, which is. It means the error is because of a different version of MYSQL from were you exporting your SQL database and where you importing also a different version of MYSQL. MySQL collation is nothing but a set of rules that are used to compare the characters in a particular character set. Unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci': This error is because the local server and live server have different versions of MYSQL. When i do a join on both tables, it works. With the COLLATE clause, you can override whatever the default collation is for a comparison. But the problem is both schemas follow different charset utf8generalci & utf8mb4unicodeci.
#Mysql collate how to#
Your comparisons should now be case-sensitive.In this post, we are going to teach you, how to fixed unknown collation utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci error In MYSQL. I want to join tables from two different schemas. `Value` VARCHAR(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin You can change your database, table, or column collation to something case sensitive as follows: - Change database collationĪLTER DATABASE `databasename` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin ĪLTER TABLE `table` CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin | myschema | mytable | latin1_swedish_ci | | table_schema | table_name | table_collation | | collation_database | latin1_swedish_ci |Īnd you can check your table collation using: mysql> SELECT table_schema, table_name, table_collationįROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_name = `mytable` ALTER DATABASE dbname CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8generalci Run the following command to change the character set and collation of your table: ALTER. | collation_connection | utf8_general_ci | You can check your server, database and connection collations using: mysql> show variables like '%collation%' Comparisons are case insensitive when the column uses a collation which ends with _ci (such as the default latin1_general_ci collation) and they are case sensitive when the column uses a collation which ends with _cs or _bin (such as the utf8_unicode_cs and utf8_bin collations).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
